Brain & Neurovascular Surgeries
- Brain & Neurovascular Surgeries
- Brain Tumor SurgeryBrain Tumor Surgery
- Skull Base Tumor SurgerySkull Base Tumor Surgery
- Neurovascular SurgeryNeurovascular Surgery
- Endovascular NeurosurgeryEndovascular Neurosurgery
- Stroke Surgery & ThrombectomyStroke Surgery & Thrombectomy
- Traumatic Brain Injury SurgeryTraumatic Brain Injury Surgery
- Pituitary Tumor SurgeryPituitary Tumor Surgery
- Hydrocephalus Surgery Hydrocephalus Surgery
- Epilepsy SurgeryEpilepsy Surgery
- Functional NeurosurgeryFunctional Neurosurgery
Traumatic Brain Injury Surgery (Clot Evacuation, Decompression)
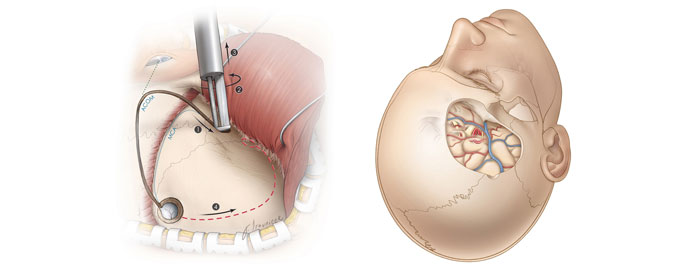
Traumatic Brain Injury Surgery is performed to manage severe head injuries that cause bleeding, swelling, or increased pressure within the skull. When a blood clot (hematoma) forms due to trauma, clot evacuation surgery is done to remove the accumulated blood and relieve pressure on the brain tissue. In cases where brain swelling is severe and life-threatening, decompressive craniectomy is performed — a portion of the skull is temporarily removed to allow the swollen brain to expand safely and prevent further damage. These surgeries are crucial to restore normal brain function, prevent secondary injury, and improve the chances of recovery in patients with major head trauma.
- Removes blood clots (epidural, subdural, or intracerebral hematomas).
- Relieves raised intracranial pressure and brain compression.
- Decompressive craniectomy allows space for the swollen brain to expand.
- Helps prevent brain herniation and further neurological damage.
- Aimed at saving life and minimizing long-term neurological deficits.
