Brain & Neurovascular Surgeries
- Brain & Neurovascular Surgeries
- Brain Tumor SurgeryBrain Tumor Surgery
- Skull Base Tumor SurgerySkull Base Tumor Surgery
- Neurovascular SurgeryNeurovascular Surgery
- Endovascular NeurosurgeryEndovascular Neurosurgery
- Stroke Surgery & ThrombectomyStroke Surgery & Thrombectomy
- Traumatic Brain Injury SurgeryTraumatic Brain Injury Surgery
- Pituitary Tumor SurgeryPituitary Tumor Surgery
- Hydrocephalus Surgery Hydrocephalus Surgery
- Epilepsy SurgeryEpilepsy Surgery
- Functional NeurosurgeryFunctional Neurosurgery
Neurovascular Surgery (Aneurysm, AVM, Carotid Surgery)
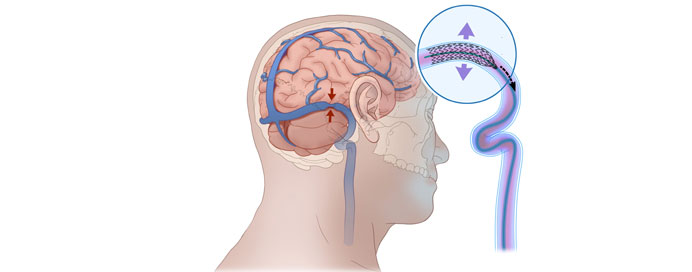
Neurovascular surgery is a specialized branch of neurosurgery that focuses on disorders of the blood vessels in the brain and spinal cord. These conditions can be life-threatening, leading to stroke, hemorrhage, or neurological deficits. Surgeons in this field manage both congenital and acquired vascular abnormalities using open microsurgical techniques or minimally invasive endovascular approaches.
Brain Aneurysm
A brain aneurysm is a weak or thin spot in a blood vessel wall in the brain that balloons out and fills with blood. It can rupture, causing subarachnoid hemorrhage, a life-threatening type of stroke.
Symptoms
- Headache
- Vision problems (double vision, drooping eyelid)
- Numbness or weakness on one side
- Seizures (rare)
Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM)
AVM is an abnormal tangle of arteries and veins in the brain or spinal cord that bypasses normal capillary beds, leading to increased risk of bleeding.
Symptoms
- Headaches
- Seizures
- Weakness or numbness
- Vision changes
- Stroke-like symptoms if it bleeds
Carotid Surgery
Carotid arteries supply blood to the brain. Carotid artery disease occurs when arteries are narrowed by atherosclerotic plaques, increasing the risk of ischemic stroke.
Symptoms of carotid stenosis
- Transient ischemic attacks (TIA): temporary weakness, vision loss, or speech difficulty
- Often asymptomatic until severe
