Brain & Neurovascular Surgeries
- Brain & Neurovascular Surgeries
- Brain Tumor SurgeryBrain Tumor Surgery
- Skull Base Tumor SurgerySkull Base Tumor Surgery
- Neurovascular SurgeryNeurovascular Surgery
- Endovascular NeurosurgeryEndovascular Neurosurgery
- Stroke Surgery & ThrombectomyStroke Surgery & Thrombectomy
- Traumatic Brain Injury SurgeryTraumatic Brain Injury Surgery
- Pituitary Tumor SurgeryPituitary Tumor Surgery
- Hydrocephalus Surgery Hydrocephalus Surgery
- Epilepsy SurgeryEpilepsy Surgery
- Functional NeurosurgeryFunctional Neurosurgery
Skull Base Tumor Surgery
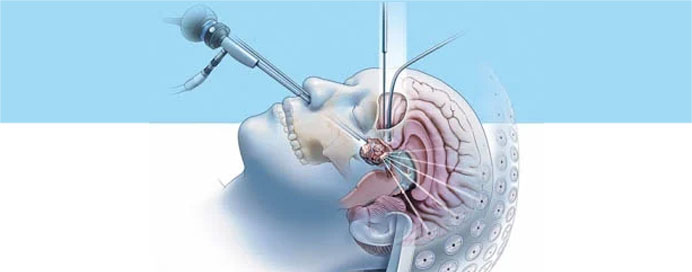
Skull base tumor surgery is a specialized neurosurgical procedure performed to remove abnormal growths located at the base of the skull, an area that separates the brain from the eyes, ears, nasal cavity, and neck. These tumors can be benign (non-cancerous) or malignant (cancerous) and are often found near vital structures such as nerves, blood vessels, and the brainstem — which makes their treatment highly complex.
The goal of the surgery is to safely remove or reduce the tumor while preserving essential brain and nerve functions such as vision, hearing, speech, and balance. Advances in microsurgical and endoscopic techniques have made these surgeries safer and more precise than ever before.
Types of Skull Base Tumors
- Meningiomas – Tumors arising from the meninges (coverings of the brain)
- Acoustic Neuromas (Vestibular Schwannomas) – Affect the hearing and balance nerve
- Pituitary Tumors – Form in the pituitary gland
- Chordomas and Chondrosarcomas – Rare tumors from bone or cartilage
- Cranial Nerve Schwannomas – Involve nerves controlling face, vision, or swallowing
- Metastatic Tumors – Spread from other parts of the body
Surgical Approaches
1- Endoscopic (Minimally Invasive) Skull Base Surgery:- Done through the nose or small openings using an endoscope (camera).
- Less pain, smaller scars, and faster recovery.
- Traditional approach where a small section of skull is opened.
- Used for large or complex tumors involving critical structures.
